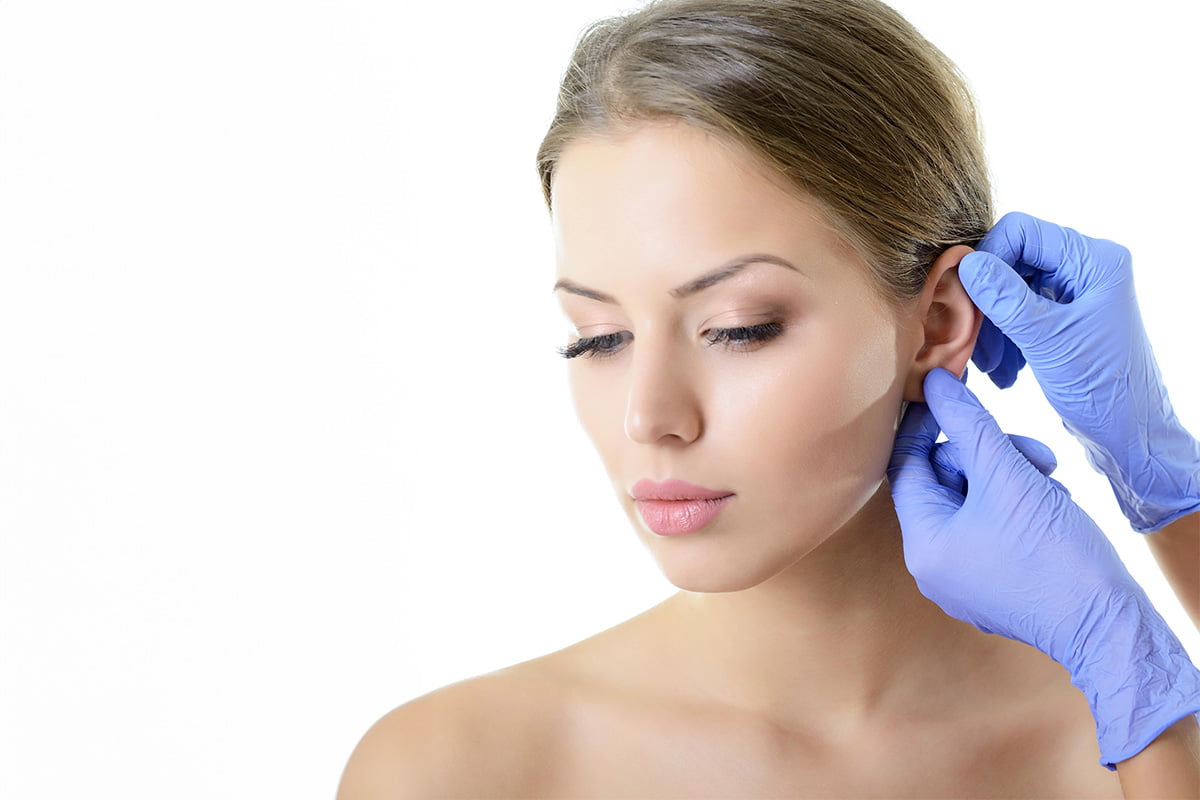
What is Otoplasty?
1. What is Otoplasty?
Otoplasty, commonly known as ear surgery, is a cosmetic procedure designed to reshape, reposition, or reduce the size of the ears. The procedure can address a variety of concerns including protruding ears, overly large ears, or other congenital or acquired ear deformities, helping to enhance facial harmony.
2. What Techniques Are Used in Otoplasty?
- Ear Pinning: This is the most common type of otoplasty, addressing ears that stick out too far from the head. Incisions are typically made behind the ear to adjust the ear’s position.
- Ear Reduction: This procedure reduces the size of the ears, either by addressing the pinna (the main outer portion of the ear) or the earlobe.
- Ear Augmentation: For individuals who have underdeveloped ears or lack an ear due to injury or birth defect, this procedure aims to build up the ear structure.
- Earlobe Repair: This addresses split or stretched earlobes, often resulting from wearing heavy earrings or trauma.
3. Who is Recommended for Otoplasty?
- Individuals bothered by the size or position of their ears.
- Those with ears that are disproportionate to the head or face.
- Individuals with a congenital ear deformity or one acquired from injury.
- Children or adults who experience teasing or self-consciousness due to the appearance of their ears.
4. When is Otoplasty Not Recommended?
- Patients with active ear infections or certain ear diseases.
- Those with unrealistic expectations about the outcome.
- Individuals in poor health or with medical conditions that could impede healing.
5. The Procedure Process
- Consultation: A thorough examination of the ears and discussion about the desired outcome.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia may be administered based on the procedure’s extent and patient preference.
- Incisions: Depending on the technique used, incisions can be made behind the ears or within the ear’s natural creases to minimize visible scarring.
- Correction: Cartilage and skin might be removed or reshaped, and sutures might be used to help the ear heal in its new position.
6. Things to Know
- Otoplasty is one of the few cosmetic procedures commonly performed on children, often around the ages of 5 to 6, when the ears have nearly reached their full size.
- The procedure can improve self-esteem and confidence.
7. Post-Operative Process
- A bandage or dressing will likely be wrapped around the head to protect and support the ears in their new position.
- Mild pain, swelling, and numbness are common but usually subside within a few days.
- It’s crucial to avoid activities that might bend or injure the ears during recovery.
- Most patients can return to school or work within a week, but physical activities, especially contact sports, should be avoided for at least a month.
- Regular follow-up appointments will ensure proper healing and address any concerns.
As always, it’s imperative to consult with a board-certified plastic surgeon experienced in otoplasty to ensure the best results and safety.
FAQs
- What age is suitable for otoplasty?
- Otoplasty can be performed on both children and adults. For children, it’s often done around the ages of 5 to 6, when the ears have nearly reached their adult size and before school age to avoid potential teasing.
- Will there be visible scars after otoplasty?
- Scars are typically concealed behind the ear or within the ear’s natural creases, making them difficult to see. Over time, any scars tend to fade and become even less noticeable.
- How long is the recovery period?
- Most patients can return to school or work within a week. However, vigorous physical activities, especially those that might impact the ears, should be avoided for several weeks.
- Is otoplasty painful?
- Patients might experience some discomfort or mild pain after the surgery, but this is usually manageable with over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medications.
- Can otoplasty be reversed?
- Otoplasty results are generally permanent. However, if a patient is unsatisfied with the results, revision surgery might be possible depending on the initial procedure and the specific concerns.
- Will otoplasty affect my hearing?
- No, otoplasty is a cosmetic procedure that reshapes the external ear. It does not affect the inner ear structures responsible for hearing.
- How long do the results of otoplasty last?
- The results of otoplasty are typically permanent. However, just like any other body part, ears can change shape or size due to aging or trauma.
- Is there a non-surgical alternative to otoplasty?
- While there are some non-surgical ear pinning devices available, they typically offer temporary results and may not be suitable for all types of ear deformities.
- Can both ears be treated in one session?
- Yes, typically both ears are addressed during one surgical session to ensure symmetry and balance.
- What are the risks associated with otoplasty?
- While otoplasty is generally safe, as with any surgery, there are risks such as infection, bleeding, scarring, asymmetry, and complications from anesthesia. Choosing a board-certified surgeon with experience in otoplasty minimizes these risks.
Remember, it’s essential to have a thorough consultation with a board-certified plastic surgeon to address individual concerns and get accurate information tailored to the patient’s specific situation.